How diamond anvil cell works up to 4 Mbar - Dr. Bing Li
Diamond anvil cell (DAC) has been used for almost 60 years to simulate extreme pressure environments, it holds the static pressure record generated in laboratories on the earth. Although some studies have demonstrated techniques to generate 4 million atmosphere pressures (400 GPa) – the generally accepted limit pressure of a conventional DAC, yet few have examined how the DAC behaves in this pressure region. Using submicron synchrotron x-ray beam, a group of scientists led by Ho-kwang Mao, director of HPSTAR (the Center of High Pressure Science and Technology Advanced Research, China) have studied the loading behavior of DAC up to 400 GPa. A universal s-shape loading behavior and unavoidable cupping were found for the conventional DAC experiments. The detailed results are reported in Proceeding of the National Academic of Sciences, USA.
DAC is a major toolthat squeezes small samples between two opposing diamonds to generate extreme high pressure,it is used in a wide area of high pressure science to explore the novel phenomena of matter with extremely high density;also as a technical problem, how to improve the DAC technique and use it to generate higher pressures is a common problem of many scientists. Previously some experimental studies explored the behavior of the DAC under high pressures, however, detailed local strain stress informationcould not be derived due to the limitation of the probe size,moreover, these studies were under relatively low pressures.
Using submicron focused synchrotron X-ray beam, the authors performed in situ high-pressure synchrotronX-ray diffraction and absorption experiments to investigatethe behavior of the DAC up to 400 GPa – a pressure that generally accepted the maximum pressure of a conventional DAC. This study provides a detailed picture of pressure loading and distribution, gasket thickness variation, and diamond anvil deformation up to 400 GPa.
“Our work showsverydetails on the loading behavior of diamond anvils under high pressures, it would be very useful for high pressure scientists to obtain ultra-high pressure using DAC.”said Dr. Bing Li, the first author on the study leading the experiment work
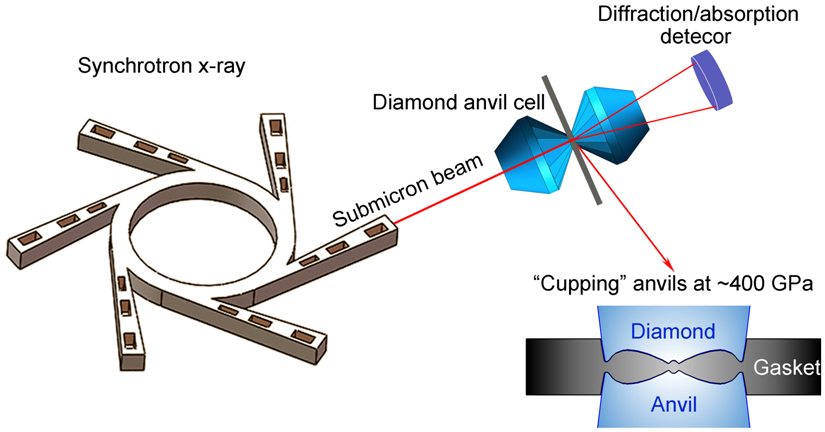 “The s-shape loading curve and cupping in both beveled and flat anvils are universal and unavoidable consequences of conventional DAC experiments,” Dr. Mao explained, “our findings can be used to improve future DAC designs and benefit the high-pressure research in the region of 400 GPa”
“The s-shape loading curve and cupping in both beveled and flat anvils are universal and unavoidable consequences of conventional DAC experiments,” Dr. Mao explained, “our findings can be used to improve future DAC designs and benefit the high-pressure research in the region of 400 GPa”
Other team members including Cheng Ji of Carnegie Institution of Washington;Wenge Yang, Junyue Wang and Jiuhua Chen of the Center of High Pressure Science and Technology Advanced Research, China;Ke Yang of Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility;Ruqing Xu, Wenjun Liu and ZhonghouCai of Advanced Photon Source.
Caption: X-ray imaging reveals diamond anvils cupping under extreme pressures. Image courtesy of Bing Li.
金刚石对顶砧压机是静态极端高压产生的主要设备,它保持着世界上产生静态压力的最高记录。对它的使用可以追溯到60年前,它的出现帮助了科学家实现了丰富的原位研究超高压力下物质行为的愿望。金刚石对顶砧压机实验技术有其自身的发展过程,从最开始的能够产生几万个大气压发展到现在的几百万个大气压经历了几十年的技术改进与创新。北京高压科学研究中心(高科)主任毛河光院士带领国际科研团队,一直致力于金刚石对顶砧压机设计与技术创新方面的研究,是最先实现百万大气压力的实验设计者和研究者。本研究中,李冰等人利用最新发展的同步辐射原位测试手段,利用亚微米X光探针,对金刚石对顶砧压机的压力加载,压强分布以及金刚石砧面在极端压力下的塑性形变进行了系统研究。最高压力达到400万大气压,此压力是公认的倒角式金刚石对顶砧压机可以产生的极限压力。此项研究结果为进一步提高加载压力改进压机设计提供了重要的实验依据,结果刊登在美国科学学院院刊上(Li及合作者,PNAS,2018).
